3.6 Graph Analysis: Rational Functions
First Derivative Test
Analyze $f'(x)$ to Identify Intervals of Increase/Decrease and Extrema on the Graph of $f(x).$
- Find $f'(x)$
- Identify all critical numbers and partitions for the function.
- Values of $x$ where$f'(x)=0$ are critical numbers.
- Values of $x$ where $f'(x)$ is undefined are partitions.
- Values of $x$ where $f(x)$ is undefined are partitions.
- Graph the critical numbers and partitions on a number line, separating the number line into intervals.
- Determine the intervals on which $f(x)$ is increasing /decreasing
- Test one point contained in the interval (do not use the end points of the interval).
- $f'(x)<0$ then the function $f(x)$ is DECREASING on the interval
- $f'(x)>0$ then the function $f(x)$ is INCREASING on the interval
- Identify local maxima and minima of $f(x)$ using the First Derivative Test.
- On the interval $(a,c)$, a local maximum occurs at $f(b)$ when $f(x)$ is increasing for all $x$ in the interval $(a,b]$ and $f(x)$ is decreasing for all $x$ in the interval $[b,c)$.
- On the interval $(a,c)$, a local minimum occurs at $f(b)$ when $f(x)$ is decreasing for all $x$ in the interval $(a,b]$ and $f(x)$ is increasing for all $x$ in the interval $[b,c)$.
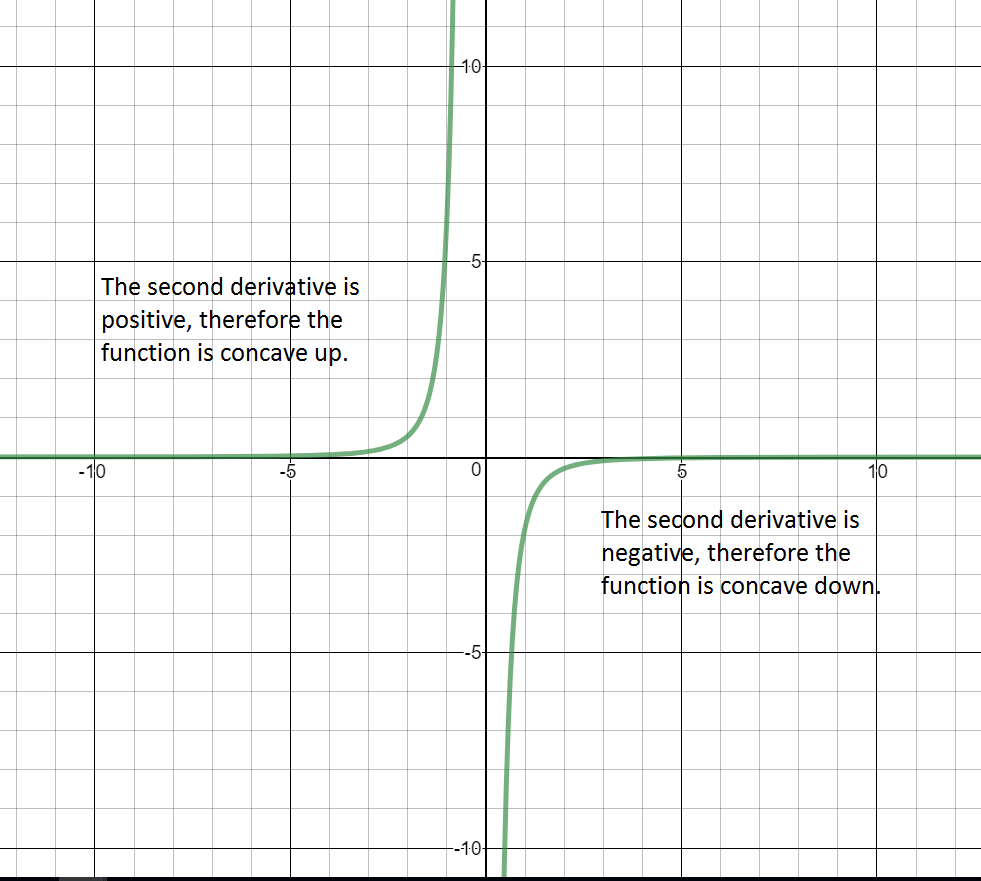
Second Derivative Test
Analyze $f''(x)$ to Identify Intervals of Concavity and Points of Inflection on the Graph of $f(x).$
- Find $f''(x).$
- Find the critical numbers for the function.
- Values of $x$ where $f''(x)=0$ are critical numbers.
- Values of $x$ where $f''(x)$ is undefined are partitions.
- Values of $x$ where $f(x)$ is undefined are partitions.
- Graph the critical numbers and partitions on a number line, separating the number line into intervals.
- Determine the intervals on which $f(x)$ is concave up or concave down.
- Test one point contained in the interval (do not use the end points of the interval).
- $f(x)$ is concave down on the interval if $f''(x)<0$.
- $f(x)$ is concave up on the interval if $f''(x)>0$.
- Identify inflection points of $f(x)$. A point of inflection occurs at $x=a$ when $f''(a)=0$ and $f''(x)$ changes concavity across $a$.
3.6 Video
Use the First & Second Derivative Tests to analyze the function. Identify x- & y-intercepts, any holes or asymptotes (if they exist), intervals of increase/decrease, extrema, interval of concavity, and inflection points on the graph of the function.
-
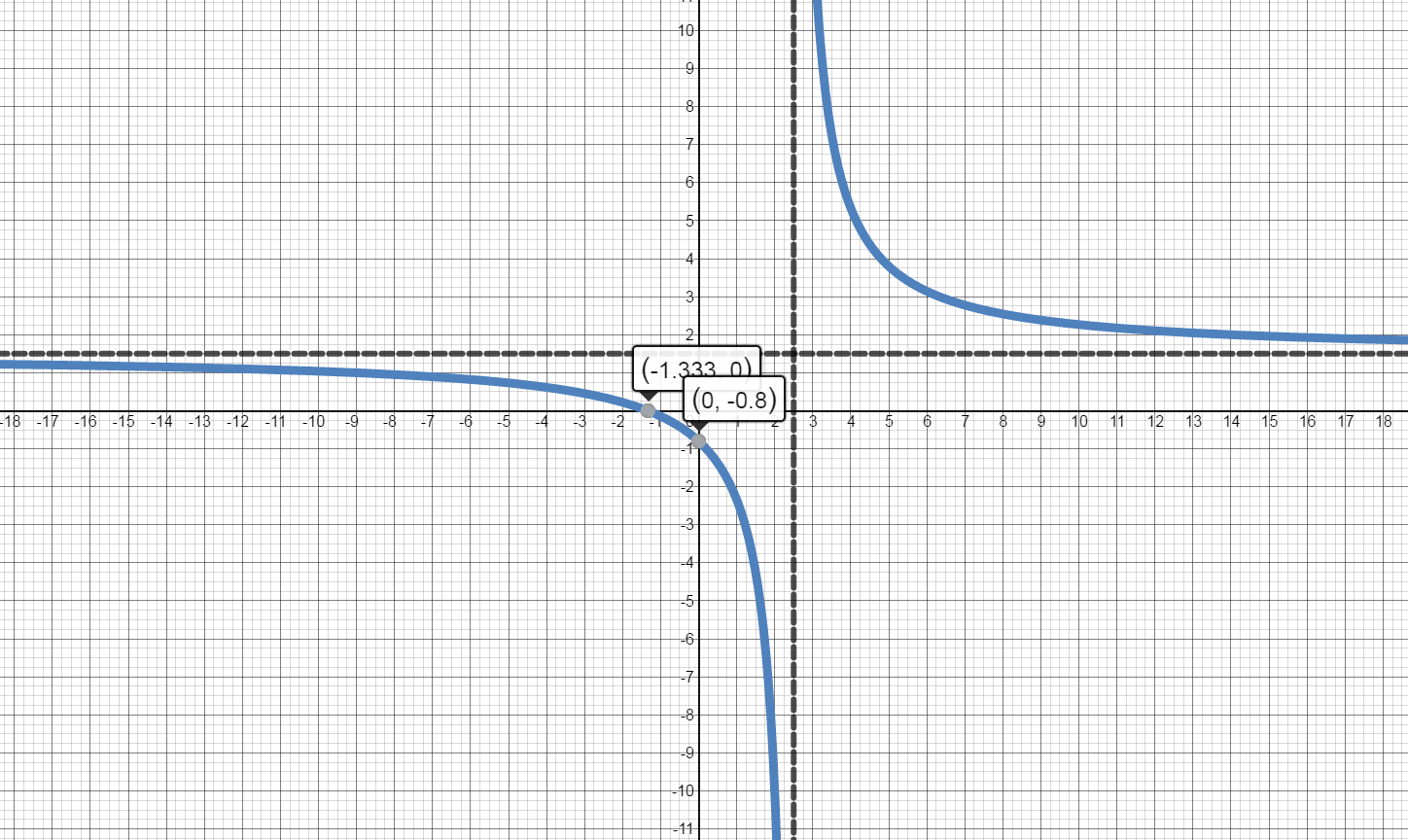
$f(x)=\frac{3x+4}{2x-5}$
-
Increasing and Decreasing
${f}'\left( x \right)=\frac{3\left( 2x-5 \right)-2\left( 3x+4 \right)}{{{\left( 2x-5 \right)}^{2}}}=\frac{6x-15-6x-8}{{{\left( 2x-5 \right)}^{2}}}=\frac{-23}{{{\left( 2x-5 \right)}^{2}}}$
Values of x where ${f}'\left( x \right)=0:$
$\frac{0}{1}=\frac{-23}{{{\left( 2x-5 \right)}^{2}}}$
$-23 \neq 0$. There are no values of x where ${f}'\left( x \right)=0.$
Values of x where ${f}'\left( x \right)$ is undefined:
$2x-5=0$, $ x=\frac{5}{2}$
Values of x where $f\left( x \right)$ is undefined:
$2x-5=0$, $x=\frac{5}{2}$
Separate into intervals using: $x=\frac{5}{2}$.
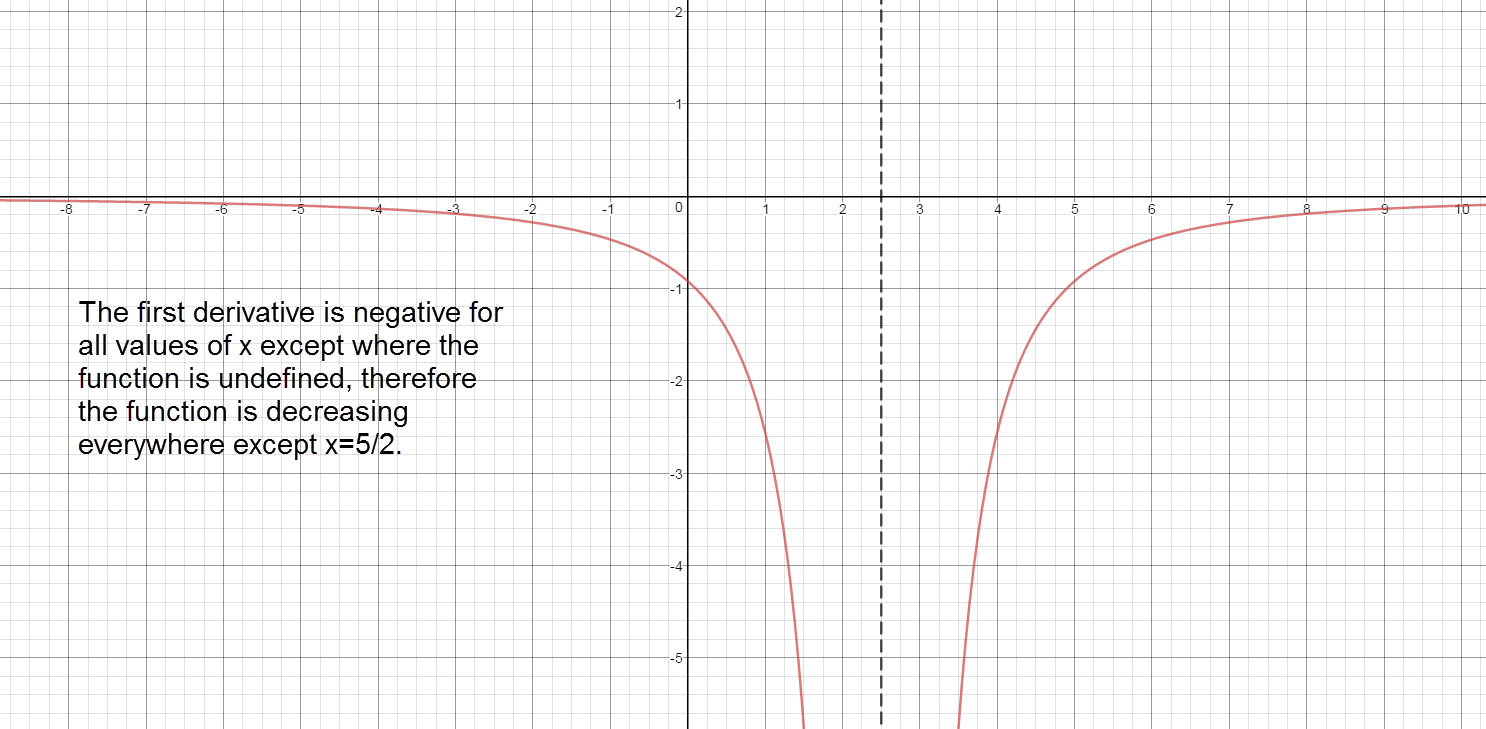
Sign graph of ${f}'(x)$ reading left to right: negative, ${f}'\left( \frac{5}{2} \right)\text{= undefined}$, negative Increasing:
The graph of the first derivative is never above the x axis. Therfore, there are no intervals where $f(x)$ is increasing.
Decreasing:
$\left( -\infty ,\frac{5}{2} \right)\cup \left( \frac{5}{2},\infty \right)$ The graph of the first derivative is always below the x axis. Therefore, the function is decreasing over the entire domain.
-
Local Maxima:
The first derivative never changes from positive to negative. There are no local maxima.
Local Minima:
The first derivative never changes from negative to positive. There are no local minima.
-
Concave Up and Concave Down
${f}''\left( x \right)=-23\left( -2 \right){{\left( 2x-5 \right)}^{-3}}\left( 2 \right)=\frac{92}{{{\left( 2x-5 \right)}^{3}}}$
Values of x where ${f}''(x)=0$:
There are no values of x where ${f}''\left( x \right)=0$.
Values of x where ${f}''\left( x \right)$ is undefined:
$ 2x-5=0$
$ x=\frac{5}{2}$
Values of x where $f\left( x \right)$is undefined:
$2x-5=0$
$x=\frac{5}{2}$
Separate into intervals using: $x=\frac{5}{2}$.
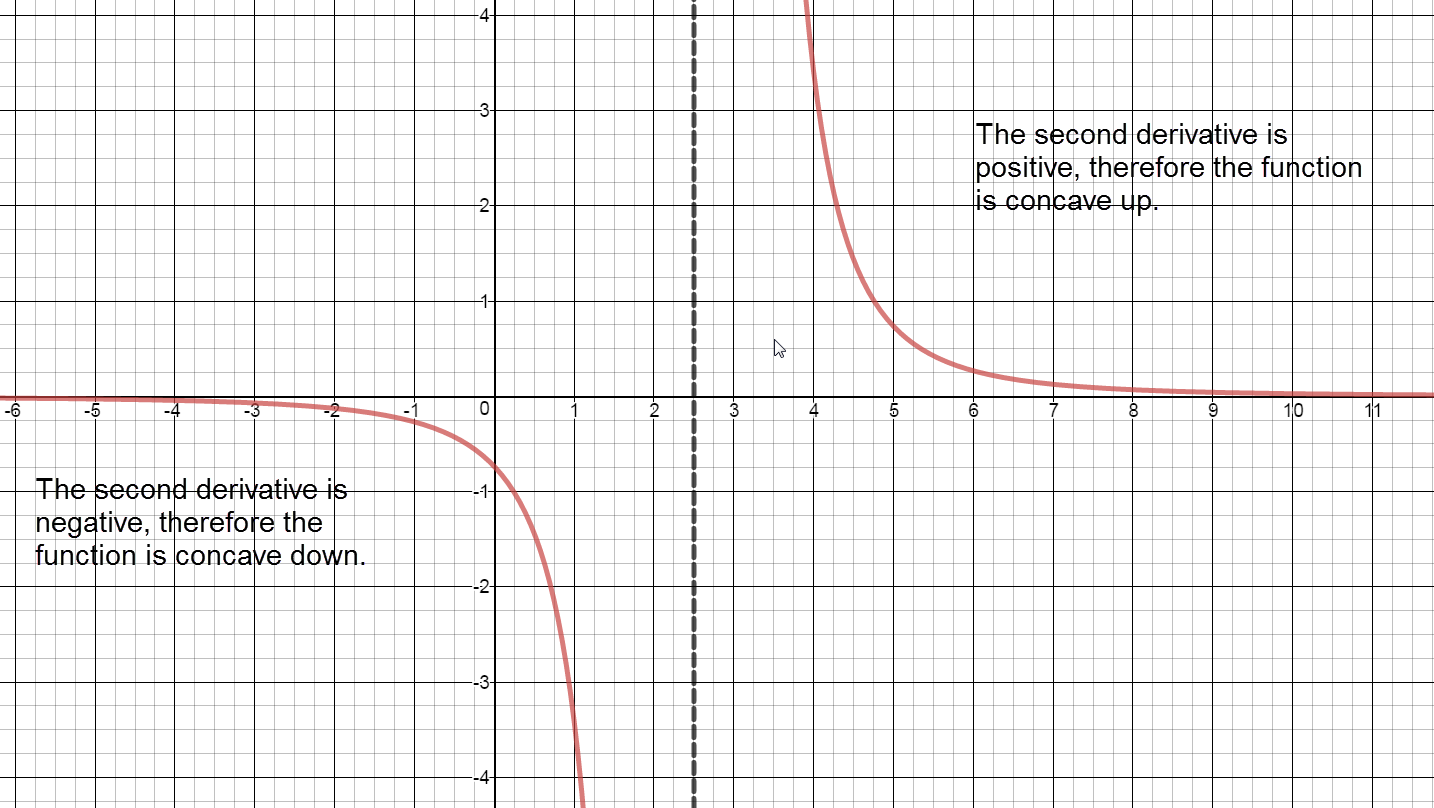
Sign chart for ${f}''\left( x \right)$: negative, ${f}''\left( \frac{5}{2} \right)=$ undefined, positive Concave up:
The graph of $f(x)$ is concave up on the interval $\left( \frac{5}{2},\infty \right).$
Concave down:
The graph of $f(x)$ is concave down on the interval $\left( -\infty ,\frac{5}{2} \right).$
-
Inflection Points:
Even though the function changes from concave down to concave up at $x=\frac{5}{2}$, there are no points of inflection because the function is undefined at $x=\frac{5}{2}.$
-
-
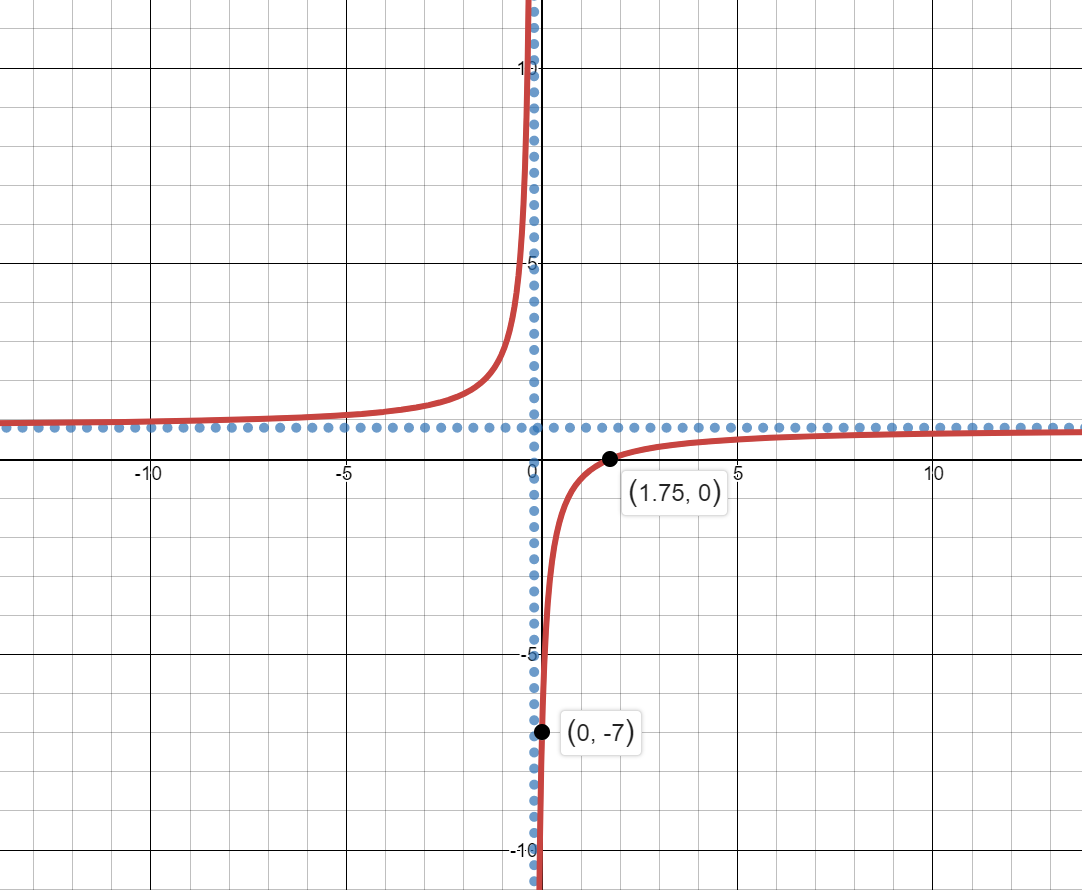
$f(x)=\frac{4x-7}{5x+1}$
-
Increasing and Decreasing
${f}'\left( x \right)=\frac{4\left( 5x+1 \right)-5\left( 4x-7 \right)}{{{\left( 5x+1 \right)}^{2}}}=\frac{20x+4-20x+35}{{{\left(5x+1 \right)}^{2}}}=\frac{39}{{{\left(5x+1 \right)}^{2}}}$
Values of x where ${f}'\left( x \right)=0:$
$\frac{0}{1}=\frac{39}{{{\left( 5x+1 \right)}^{2}}}$
$39 \neq 0$. There are no values of x where ${f}'\left( x \right)=0.$
Values of x where ${f}'\left( x \right)$ is undefined:
$5x+1=0$, $ x=-\frac{1}{5}$
Values of x where $f\left( x \right)$ is undefined:
$5x+1=0$, $ x=-\frac{1}{5}$
Separate into intervals using: $x=-\frac{1}{5}$.
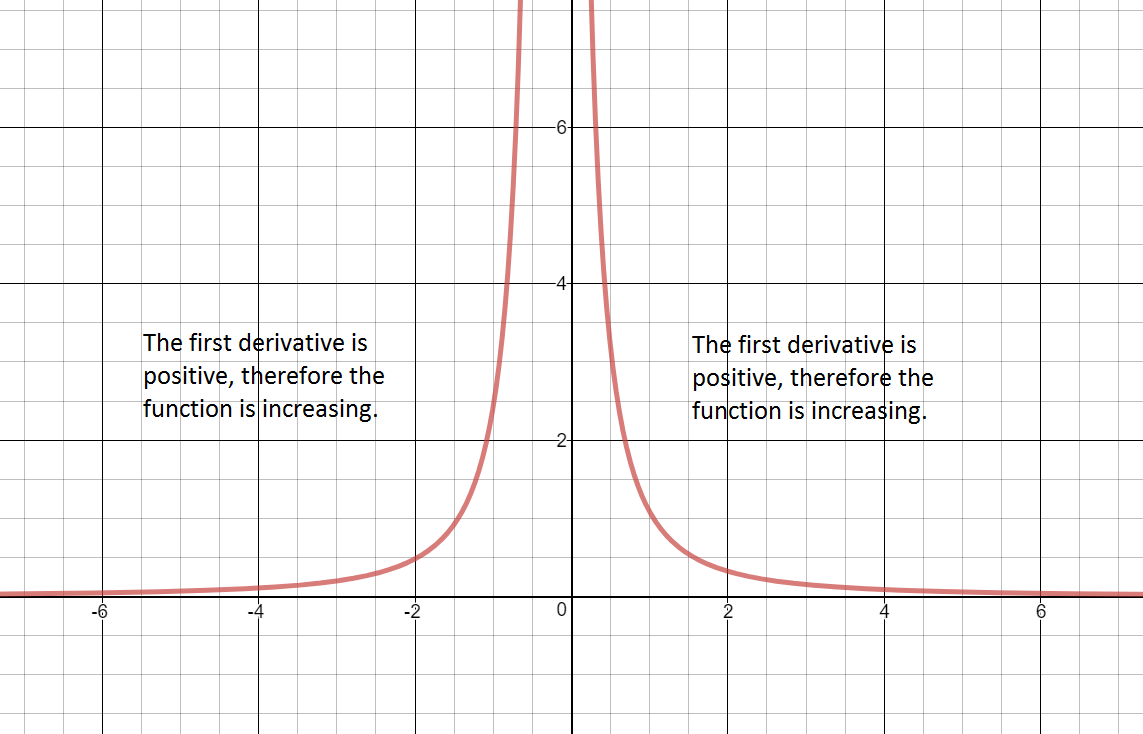
Sign graph of ${f}'(x)$ reading left to right: positive, ${f}'\left( -\frac{1}{5} \right)\text{= undefined}$, positive Increasing:
$\left( -\infty ,-\frac{1}{5} \right)\cup \left( -\frac{1}{5},\infty \right)$ The graph of the first derivative is always above the x axis. Therefore, the function is increasing over the entire domain.
Decreasing:
The graph of the first derivative is always above the x axis. Therfore, there are no intervals where $f(x)$ is decreasing.
-
Local Maxima:
The first derivative never changes from positive to negative. There are no local maxima.
Local Minima:
The first derivative never changes from negative to positive. There are no local minima.
-
Concave Up and Concave Down
${f}''\left( x \right)=39\left( -2 \right){{\left( 5x+1 \right)}^{-3}}\left( 5 \right)=-\frac{390}{{{\left( 5x+1 \right)}^{3}}}$
Values of x where ${f}''(x)=0$:
There are no values of x where ${f}''\left( x \right)=0$.
Values of x where ${f}''\left( x \right)$ is undefined:
$ 5x+1=0$
$ x=-\frac{1}{5}$
Values of x where $f\left( x \right)$is undefined:
$5x+1=0$
$x=-\frac15$
Separate into intervals using: $x=-\frac{1}{5}$.
Sign chart for ${f}''\left( x \right)$: positive, ${f}''\left( -\frac{1}{5} \right)=$ undefined, negative Concave up:
The graph of $f(x)$ is concave up on the interval $\left( -\infty ,-\frac{1}{5} \right).$
Concave down:
The graph of $f(x)$ is concave down on the interval $\left( -\frac{1}{5},\infty \right).$
-
Inflection Points:
Even though the function changes from concave up to concave down at $x=-\frac{1}{5}$, there are no points of inflection because the function is undefined at $x=-\frac{1}{5}.$
-
-
$f(x)=\frac{x^2+2x-8}{x+5}$
-
Increasing and Decreasing
${f}'(x)=\frac{(2x+2)(x+5)-1(x^2+2x-8)}{(x+5)^2}=\frac{2x^2+10x+2x+10-x^2-2x+8}{(x+5)^2}=\frac{x^2+10x+18}{(x+5)^2}$
Values of x where ${f}'\left( x \right)=0:$
$\frac{0}{1}=\frac{x^2+10x+18}{(x+5)^2}$
$x^2+10x+18=0$
This will not factor so use Desmos.com
$ {f}'(x)=0$ at $x=-7.646$ and $x=-2.354$
Values of x where ${f}'(x)$ is undefined:
$x+5=0$, $ x=-5$
Values of x where $f(x)$ is undefined:
$x+5=0$, $ x=-5$
Separate number line into intervals using: $x=-7.646, -5, and -2.354$.
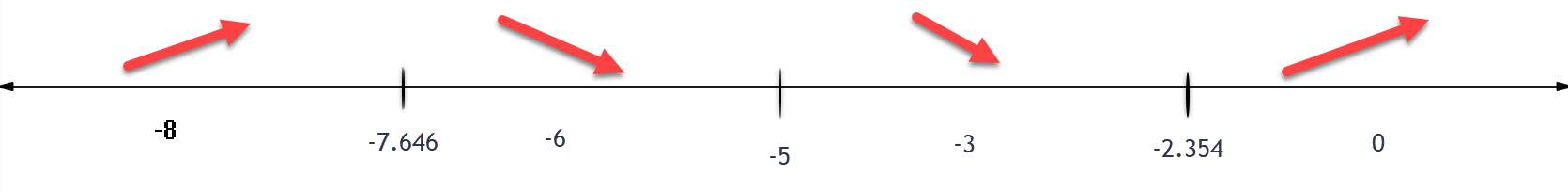
Increasing: $(-\infty,-7.646)$ U $(-2.354,\infty)$
Decreasing: $(-7.646, -5)$ U $(-5, -2.354)$
-
Local Maxima:
$(-7.646, -13.292)$
Local Minima:
$(-2.354, -2.708)$
-
Concave Up and Concave Down
${f}''=\frac{(2x+10)(x+5)^2-2(x+5)(x^2+10x+18)}{(x+5)^4}$
${f}''=\frac{(2x+10)(x+5)-2(x^2+10x+18)}{(x+5)^3}$
${f}''=\frac{2x^2+10x+10x+50-2x^2-20x-36}{(x+5)^3}$
${f}''=\frac{14}{(x+5)^3}$
Values of x where ${f}''(x)=0$:
There are no values of x where ${f}''\left( x \right)=0$.
Values of x where ${f}''(x)$ is undefined:
$ x+5=0$
$ x=-5$
Values of x where $f\left( x \right)$is undefined:
$x+5=0$
$x=-5$
Separate into intervals using: $x=-5$.
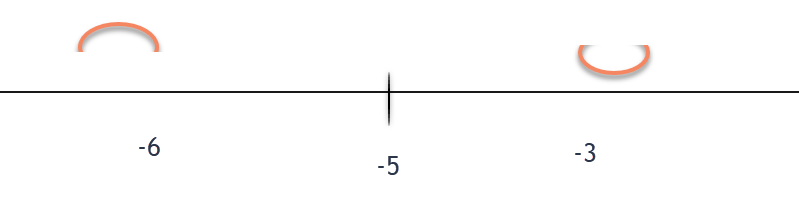
The graph of $f(x)$ is concave up on the interval $( -5 , \infty).$
Concave down:
The graph of $f(x)$ is concave down on the interval $( -\infty, -5).$
-
Inflection Points:
Even though the function changes from concave up to concave down at $x=-5$, there are no points of inflection because the function is undefined at $x=-5.$
-
-
Construct a sketch of the graph of a function of $f$ that has the given properties.
- $f(x)$ is such that
- $f'(5)=0$
- $f'(x)< 0$ on the interval $(-\infty,5)$
- $f'(x)>0$ on the interval $(5,\infty)$
- $f''(x)>0$ on the interval $(-\infty,\infty)$
-
- $f(0)=2$
- $f'(-3)=0$ and $f'(4)=0$
- $f'(x)<0$ on the interval $(-3,4)$
- $f'(x)>0$ on the intervals $(-\infty,-3)$ and $(4,\infty)$
- $f''(x)<0$ on the interval $(-\infty,0)$
- $f''(x)>0$ on the interval $(0,\infty)$

-
- $f(4)$ is undefined
- $f'(4)$ is undefined
- $f''(4)$ is undefined
- $f(0)=0$
- $f'(x)<0$ on the intervals $(-\infty,4)$ and $(4,\infty)$
- $f'(x)>0$ nowhere
- $f''(x)<0$ on the interval $(-\infty,4)$
- $f''(x)>0$ on the interval $(4, \infty)$
- $f(x)$ is such that
-
$f(x)=\sqrt[3]x-x$
-
Increasing and Decreasing
${f}'(x)=\frac13x^\frac{-2}3-1=\frac1{3\sqrt[3]{x^2}}-1$
Values of x where ${f}'\left( x \right)=0:$
$\frac{0}{1}=\frac1{3\sqrt[3]{x^2}}-1$
$\frac1{3\sqrt[3]{x^2}}=1$
$3\sqrt[3]{x^2}=1$
$\sqrt[3]{x^2}=\frac13$
$x^2=\frac1{27}$
$x=\pm\sqrt{\frac1{27}}$
$ {f}'(x)=0$ at $x=-0.192$ and $x=0.192$
Values of x where ${f}'(x)$ is undefined:
$\sqrt[3]{x^2}=0$, $ x=0$
Values of x where $f(x)$ is undefined:
There is nowhere that $f(x)$ is undefined
Separate number line into intervals using: $x=-0.192, x=0, x=0.192$.
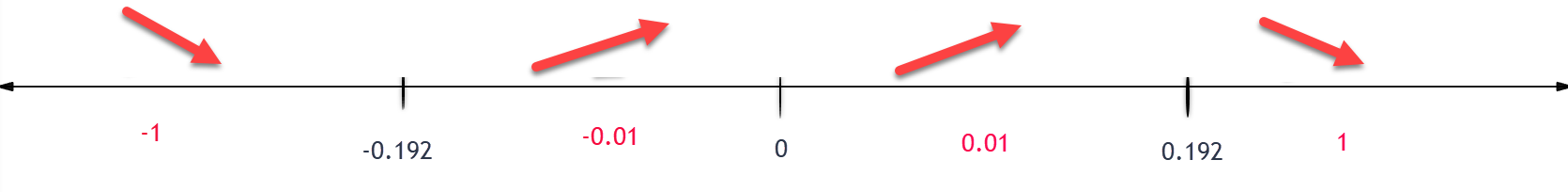
Increasing: $(-0.192,0)$ U $(0,0.192)$
Decreasing: $(-\infty, -0.192)$ U $(0.192, \infty)$
-
Local Maxima:
$(0.192, 0.385)$
Local Minima:
$(-0.192, -0.385)$
-
Concave Up and Concave Down
${f}''(x)=-\frac23\left(\frac13x^{\frac{-2}3-1}\right)=-\frac29x^\frac{-5}3$
${f}''(x)=-\frac2{9\sqrt[3]{x^5}}$
Values of x where ${f}''(x)=0$:
$-\frac2{9\sqrt[3]{x^5}}=\frac01$.
$-2=0$.
There are no critical values for ${f}''(x)$ .
Values of x where ${f}''(x)$ is undefined:
$\sqrt[3]{x^5}=0$
$ x=0$
Values of x where $f\left( x \right)$is undefined:
There are no values of x where $f\left( x \right)$is undefined.
Separate into intervals using: $x=0$.
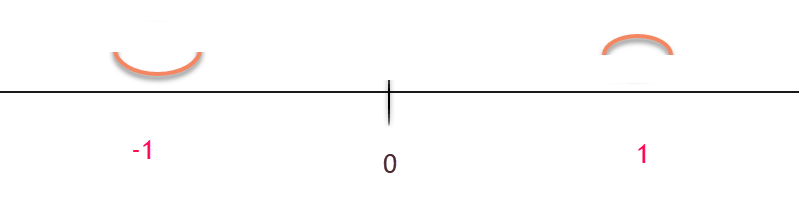
Concave up:
The graph of $f(x)$ is concave up on the interval $( -\infty, 0).$
Concave down:
The graph of $f(x)$ is concave down on the interval $( 0 , \infty).$
-
Inflection Points:
Even though the function changes from concave up to concave down at $x=0$, there is no point of inflection because the second derivative is undefined at $x=0.$
-
3.6 Lecture
Use the First & Second Derivative Tests to analyze the function. Identify x- & y-intercepts, any holes or asymptotes (if they exist), intervals of increase/decrease, extrema, interval of concavity, and inflection points on the graph of the function.
3.6 Group Work
Use the First & Second Derivative Tests to analyze the function. Identify x- & y-intercepts, any holes or asymptotes (if they exist), intervals of increase/decrease, extrema, interval of concavity, and inflection points on the graph of the function.
3.6 Additional Practice
Use the First & Second Derivative Tests to analyze the function. Identify x- & y-intercepts, any holes or asymptotes (if they exist), intervals of increase/decrease, extrema, interval of concavity, and inflection points on the graph of the function.